Dogs can gain unhealthy weight, like humans. Obesity in dogs is really harmful for their health and reduce their life quality. Checking if your dog is heavier than should be is the first step. Look at your dog from the side and above.
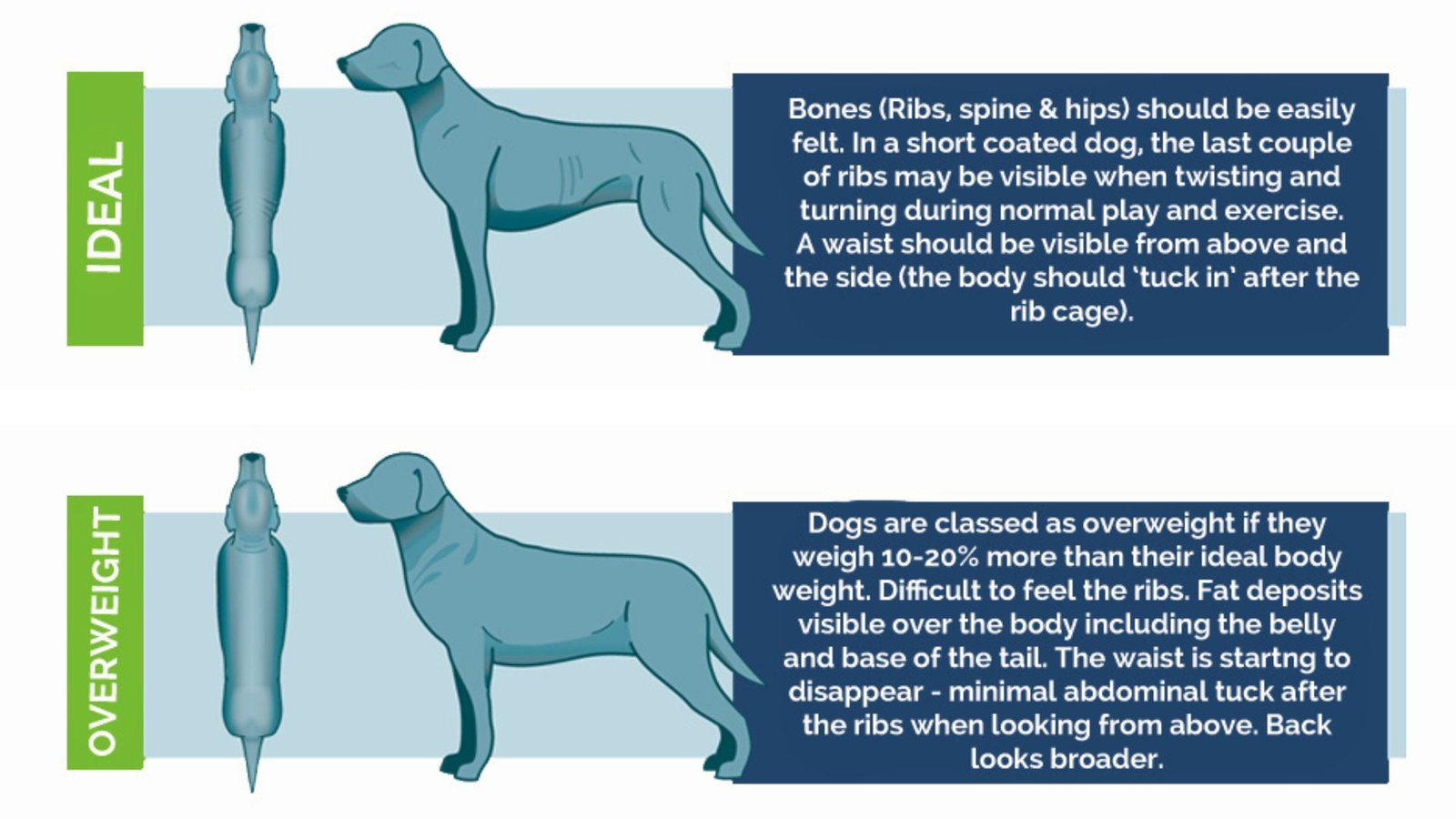
IS MY DOG FAT?
From the side, see if your dog’s waist curves inward behind the rib cage. Healthy dogs have a tucked waistline. If your dog’s waist is straight or bulges, it may be heavier and need tailored schedule.
Inspect your dog body
From above, you should notice your dog’s waist narrows behind the ribs toward the hips. If your dog looks rounded or cylindrical, that could mean excess weight. Looks can give clues, but each dog is unique. Breed, age, and body type affect healthy weights. If unsure, consult your vet.
The Dangers of Dog Obesity
Being too heavy can badly affect a dog’s health. Like humans, fat dogs have higher risks of getting sick.
They may suffer from:
- Joint pains and arthritis
- Heart troubles
- Diabetes
- Breathing issues
- Shorter lifespan
Learn more about obesity-related diseases below. Furthermore, fat dogs cannot play well. It reduces their life quality. They feel tired and uncomfortable due to extra weight. Thus, heavy dogs often become lazier, making them fatter.
Why Do Dogs Become Fat?
Many factors cause dog obesity.
These include:
- Overfeeding: Giving dogs too much food leads to weight gain. Pet owners often misjudge their dog’s calorie needs. Also, treats and table scraps pack on pounds.
- Lack of exercise: Inactive dogs are likely to become fat. Regular playtime keeps pups fit
- Genetics: Some breeds easily put on weight. Their genes make it hard to stay slim.
- Illnesses: Certain diseases like thyroid disorders cause weight issues. See a vet if your dog seems unhealthy.
Keeping Dogs Fit and Healthy
Preventing dogs from gaining too much weight needs proper food and exercise.
Here are some tips to keep your dog at a healthy weight:
- Give the right food amount. Make sure you feed your dog the proper amount for its age, size, and activity level. Ask your vet how much and how often to feed.
- Feed a balanced diet. Give your dog high-quality food with all the nutrients it needs. Avoid too many treats or table scraps, as these can make dogs gain weight.
- Exercise regularly. Take your dog for walks, play, or try activities like agility training daily. Exercise burns calories and keeps dogs healthy in body and mind.
- Set meal times. Don’t leave food out all day for your dog to eat freely. Give set meals and remove uneaten food after a while. This prevents overeating.
- Ask your vet for help. If unsure about your dog’s weight or how to manage it, ask your vet. They can give advice based on your dog’s needs.
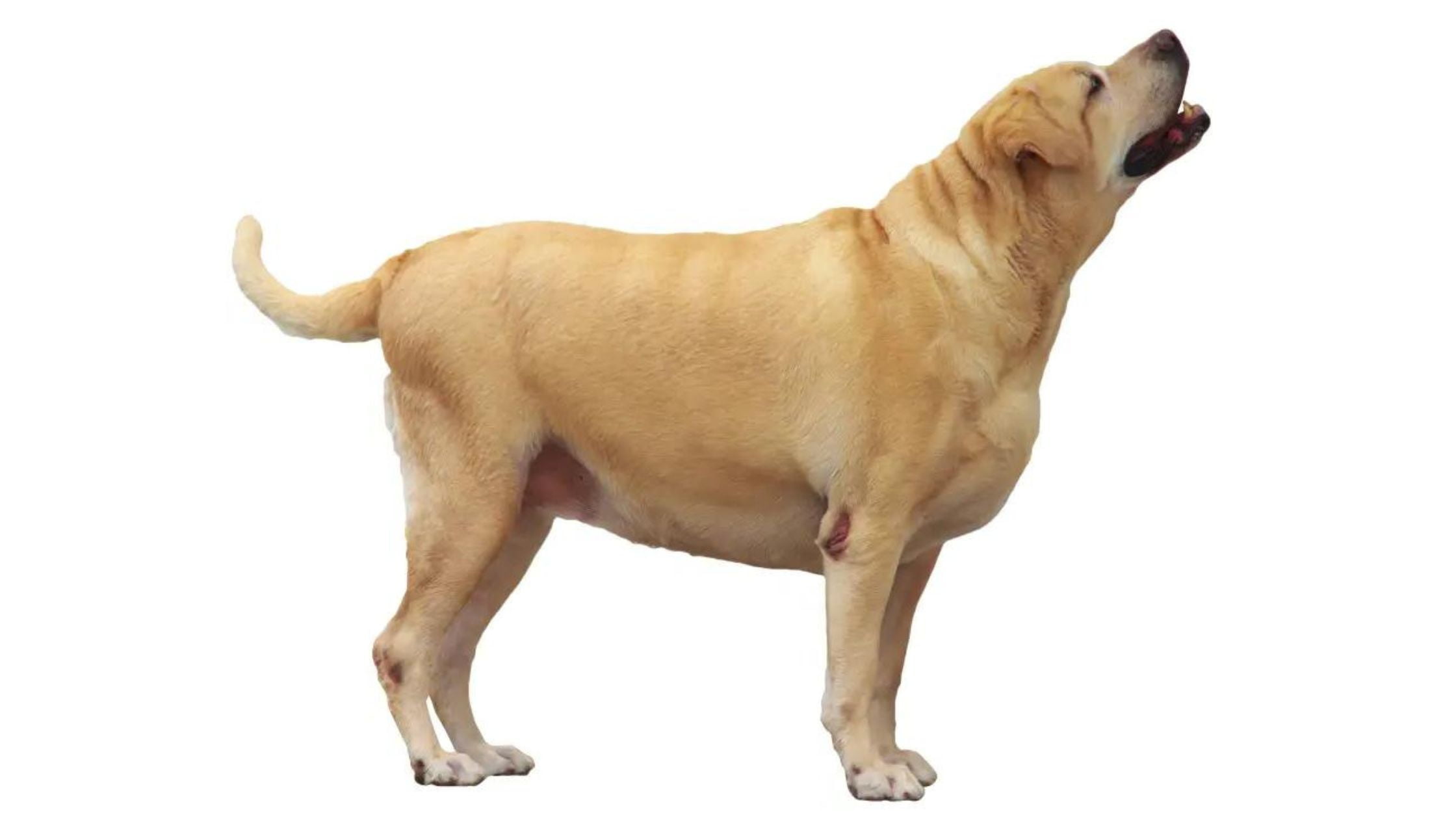

HELP YOUR DOG TO LOSE WEIGHT
If your dog is heavier, it is important to take action to help them lose weight and improve their overall health. Just like humans, dogs can suffer from various health issues due to excess weight, including joint problems, heart disease, and diabetes. Consulting with your veterinarian is the first step in creating a weight loss plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Consult your veterinarian to create a diet and exercise plan
Before starting any weight loss program for your dog, it is crucial to consult with your veterinarian. They will be able to assess your dog’s current health status, identify any underlying medical conditions, and determine the ideal weight for your dog. Your vet will also help you create a diet and exercise plan that is safe and effective for your dog’s individual needs.
Adjust your dog’s diet
One of the most important aspects of weight loss for dogs is adjusting their diet. Your vet may recommend a specific type of dog food that is lower in calories and fat. It is important to follow their guidance and avoid giving your dog table scraps or high-calorie treats. Instead, opt for healthy snacks such as carrots or green beans.
Additionally, you may need to measure your dog’s food portions to ensure they are not overeating. Feeding your dog smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can also help to keep their metabolism active and prevent overeating.
Increase your dogs exercise
Daily exercise helps dogs lose weight. Start by slowly increasing exercise time and effort. This can include brisk walks, running, fetch games, or swimming. Choose activities suitable for your dog’s breed, age, and fitness level. If your dog has health issues or joint problems, ask your vet for the best exercise plan.
Monitor your dogs progress
Weigh your dog regularly and observe changes in body shape and energy levels. This shows if the diet and exercise are working well. If your dog isn’t losing weight or has health issues, talk to your vet to adjust the weight loss plan.
Provide mental stimulation for your dog
Besides physical exercise, give your dog mental stimulation. Boredom can cause overeating. Keep your dog’s mind engaged with puzzle toys, interactive games, and daily training sessions. Mental stimulation prevents dogs from seeking comfort in food and reduces the risk of overeating.
Avoid crash diets for your dogs
While you want quick results, avoid crash diets for your dog. Rapid weight loss can harm their health and cause nutrient deficiencies. Focus on gradual, steady weight loss. Your vet will guide you on the appropriate rate of weight loss and ensure your dog gets necessary nutrients.
Stay consistent with the dogs program and seek support to Battle Obesity
Consistency is key when it comes to helping your dog lose weight. Stick to the diet and exercise plan recommended by your vet and avoid deviating from it. It may take time to see significant results, but with patience and consistency, your dog will gradually reach a healthier weight.
If you are finding it challenging to help your dog lose weight on your own, consider seeking support from a professional dog trainer or joining a weight loss program specifically designed for dogs. Remember that these resources can always provide additional guidance, motivation, and accountability.

THE IMPACT OF OBESITY ON DOGS: HEALTH RISKS AND POTENTIAL CONSEQUENCES
Obesity is a growing concern not only among humans but also among our beloved pets, including dogs. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of bigger and heavier dogs. This rise in dog obesity has raised questions about the potential health risks and consequences associated with excess weight in dogs. Let’s explore further what happens to heavier dogs and the impact it can have on their overall well-being and life span.
Understanding Obesity in Dogs
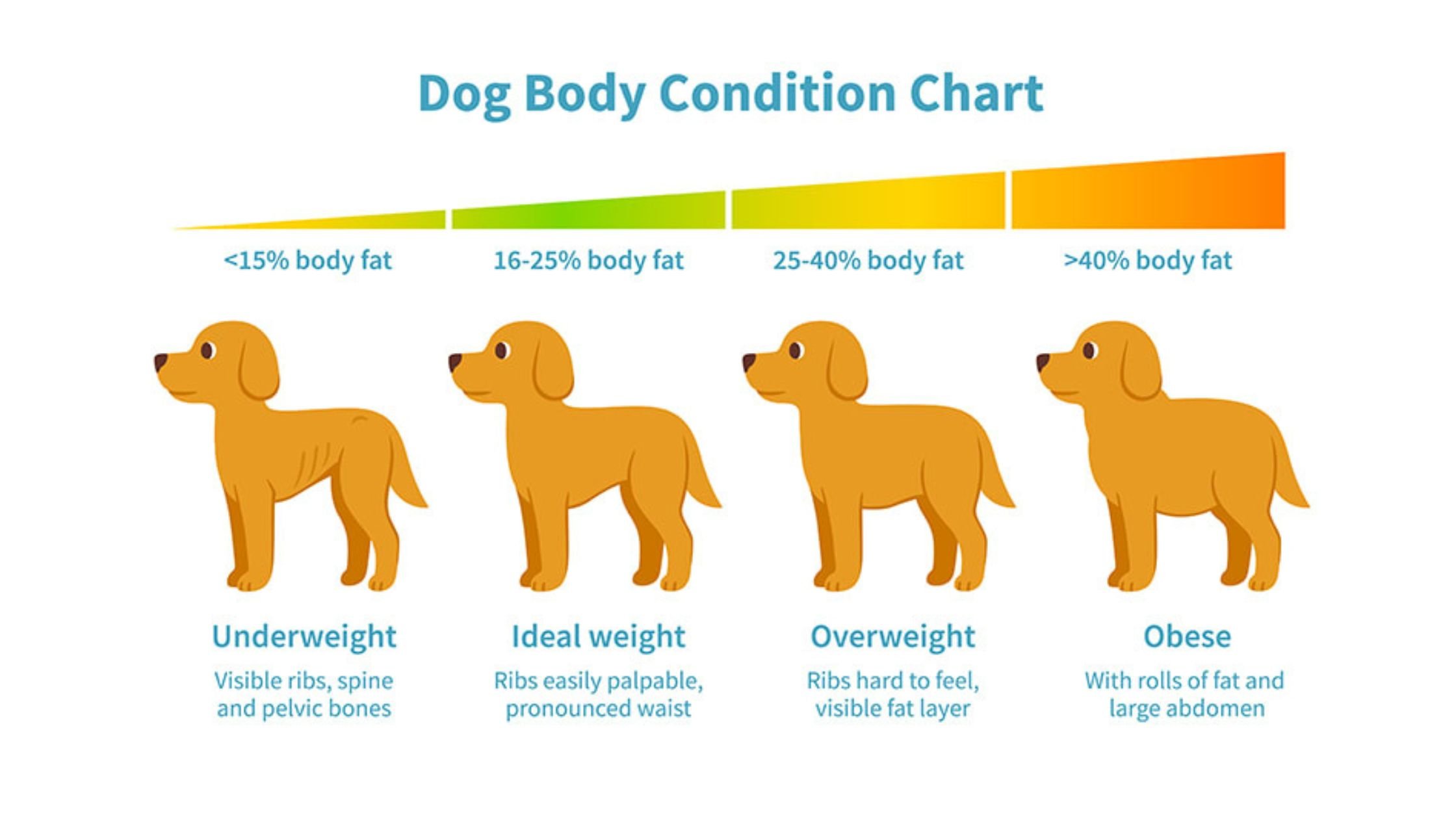
Before delving into the effects of obesity on dogs, it is important to understand what canine obesity entails. Obesity is defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat, often resulting from an imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure. Just like in humans, obesity in dogs is primarily caused by overfeeding and lack of physical activity.
Obesity can affect dogs of all breeds, ages, and sizes. However, certain factors such as genetics, age, sex, and underlying health conditions can increase a dog’s susceptibility to becoming bigger and heavier. Additionally, certain dog breeds, such as Labradors, Beagles, and Cocker Spaniels, are more prone to weight gain.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity in Dogs
Obesity in dogs poses numerous health risks, significantly impacting their overall well-being and quality of life.
Here are some of the common health risks associated with dog obesity:
- Diabetes: Obesity increases the risk of developing diabetes in dogs. Just like in humans, excess weight can lead to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism, eventually resulting in diabetes. Canine diabetes requires lifelong management and can have a significant impact on a dog’s quality of life.
- Heart Disease: Bigger and heavier dogs are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, including hypertension (high blood pressure) and congestive heart failure. The excess weight places additional strain on the heart, leading to cardiovascular problems that can be life-threatening.
- Respiratory Problems: Excess weight can cause respiratory problems in dogs, particularly brachycephalic breeds (dogs with short noses and flat faces). Obesity exacerbates breathing difficulties and increases the risk of conditions such as laryngeal collapse and obstructive airway syndrome.
- Joint Issues: Obesity puts additional stress on a dog’s joints, increasing the risk of developing musculoskeletal problems such as arthritis. The excess weight worsens joint inflammation and can lead to chronic pain and reduced mobility.
- Cancer: While the direct link between obesity and cancer in dogs is still being studied, several types of cancer have been associated with excess weight. Dogs on the heavier side are more prone to developing certain cancers, including mammary tumors, bladder cancer, and skin tumors.
Heavier Dogs Have More Reduced Life Span
Studies have shown that obesity can shorten a dog’s life span. Bigger and heavier dogs are more susceptible to developing various health conditions that can significantly impact their longevity. These conditions include diabetes, heart disease, respiratory problems, joint issues, and certain types of cancer.
The Importance of Weight Management for Dogs
Given the potential health risks associated with obesity in dogs, weight management is crucial for maintaining their overall health and well-being.
You should consider this:
Feeding your dog a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for weight management. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate portion sizes and choose high-quality dog food that meets your dog’s specific nutritional needs.
Regular exercise is vital for maintaining a healthy weight in dogs. Engage your dog in daily physical activities such as walks, playtime, and interactive games. The type and duration of exercise may vary based on your dog’s age, breed, and overall health condition.
Avoid Overfeeding Your Dogs to Prevent Obesity
Avoid overfeeding your dog and refrain from giving excessive treats or table scraps. Stick to a feeding schedule and measure the appropriate amount of food to prevent over consumption. Regularly monitor your dog’s weight and body condition. Consult with your veterinarian for guidance on maintaining an ideal body weight for your dog’s breed and size.
They can provide recommendations on weight loss strategies if necessary. If you suspect that your dog have higher weight, consult with your veterinarian. They can assess your dog’s overall health, provide guidance on weight management, and suggest any necessary dietary changes or interventions.
How to Protect your dogs from obesity?
Obesity in dogs is a serious health concern that can have significant consequences on their overall well-being and life span. The health risks associated with dog obesity are numerous, ranging from diabetes and heart disease to respiratory problems and joint issues.
Therefore, it is essential for dog owners to prioritize weight management through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and veterinary guidance. By taking proactive measures to prevent and address obesity, we can help our furry friends live healthier, happier, and longer lives.
Helping your dog lose weight is a crucial step in improving their overall health and well-being. By consulting with your veterinarian, adjusting their diet, increasing their exercise, monitoring their progress, providing mental stimulation, avoiding crash diets, staying consistent, and seeking support when needed, you can create an effective weight loss plan for your furry friend.
Final Thougts on obesity in dogs
Dogs are different, so losing weight needs a special plan. You can help your dog get healthier and happier with hard work. Check if your dog is too heavy by looking at them from the side and above. But you should talk to a vet to be sure and get help with losing weight. The right food, exercise, and vet care can keep your dog at a good weight and happier life.

FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ)
Learn more about this dog issue!
Check WikiWand for details!









