
Welcoming a puppy as the newest addition to your family can be a truly exciting and unforgettable feeling. You’d have tremendous love for that pup, as you’ll be its whole life, while it is going to be a part of the best decade of yours. As pet owners, we hate to think about our pets getting sick or dying, however, that’s only natural. What’s not natural, and is often heartbreaking is to see our furry pets struggle through life, especially from neurological diseases- silent, but extremely progressive. Neurological diseases in dogs, while not as commonly discussed as other health issues, can have a significant impact on a dog’s quality of life.
These disorders affect the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerve fibers, resulting in symptoms that range from subtle changes in behavior to severe physical disabilities. Early detection and treatment are your best shot at managing these chronic diseases in dogs. This article will explore the top five common neurological diseases in dogs related to the nervous system, highlighting symptoms, treatments, and the importance of vigilance for pet owners.

Common Neurological Diseases in Dogs
Neurological conditions afflicting dogs vary in terms of complexity and severity. Some affect motor activity while others impact cognitive or emotional health. The following five conditions represent some of the worrisome neurological diseases in dogs as they significantly impede movement, behavior, or even breathing ability.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological diseases in dogs, affecting their nervous system and leading to repeated seizures. These seizures happen because there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain which interferes with normal metabolic regulation and movement control.
Pets living with epilepsy may experience seizures that range from mild tremors to full-body convulsions. Loss of consciousness, drooling, and uncontrollable shaking are the most typical indicators, while some dogs might exhibit changes in personality or behavior before having one such as increased anxiety or irritation.
When it comes to treatment, like human epilepsy, dog epilepsy cannot be cured. However, it can be controlled with medication to control the frequency and intensity of seizures. Common anti-seizure agents include phenobarbital or potassium bromide. Pet owners should ensure regular vet checks as well as food changes to manage this chronic disease effectively.
Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD)
Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD) affects the spinal cord of breeds like French bulldogs which tend to experience back problems. This condition occurs when cushioning discs between the vertebrae deteriorate, which places additional stress on vital nerve fibers resulting in pain or paralysis.
Dogs suffering from IVDD often exhibit signs of back pain, unwillingness to jump or move freely, and even paralysis of the hind limbs in severe cases. Their tail may drop, and some dogs struggle with house-training as their bladder control decreases significantly.
Whilst treatment options depend upon the severity of an animal’s condition, rest and anti-inflammatory drugs may help alleviate some symptoms in mild cases. In more serious instances, the dog may need surgery to relieve the pressure on the spinal cord. Physical therapy can also help your furry friend regain motor activity post-surgery, improving its overall mobility and quality of life.
Canine Degenerative Myelopathy
Canine degenerative myelopathy is a progressive condition affecting the spinal cord that leads to progressive paralysis in older dogs. It is one of the most common diseases in dogs from the German Shepherd breed. Although unknown at present, its genetic component could possibly play a part in its progression.
Dogs suffering from degenerative myelopathy display hind leg weakness, difficulty walking, and eventually loss of function in both back legs. As this disease progresses, movement may become difficult as their physical limitations increase while mental and emotional well-being decline due to physical restrictions.
There is no cure for this disease. However, physical therapy and supportive care may help manage its progression and extend the quality of life for affected pets. Mobility aids like carts may assist them as the disease worsens.
Vestibular Disease
Dog vestibular syndrome also referred to as idiopathic vestibular disease, affects balance and coordination in dogs. The source may either be central (brain-related) or peripheral vestibular disease (ear-related), making older pets especially prone to this condition.
A few common signs of this disease include head tilts, loss of balance, and difficulty walking. In extreme cases, dogs may appear disoriented or even fall. Some of the symptoms are common with Parkinson’s disease in humans.
In many instances, idiopathic vestibular disease resolves on its own within several weeks. Supportive care such as providing anti-nausea medication and monitoring the dog for potential episodes of dizziness are often used. Moreover, every ear infection should be taken seriously and resolved promptly.
Brain Tumors
Brain tumors in dogs represent another serious neurological disorder that can significantly impair their neurological system function. Tumors press against parts of the brain responsible for movement, breathing, and other vital bodily processes, causing them to malfunction resulting in various kinds of complications for them and leading to various signs.
Changes in behavior, difficulty moving and seizures are hallmarks of brain tumors in dogs. Some may even suffer coordination difficulties or blindness as their brain tumor grows bigger- ultimately leading to significant health concerns as a result of its progression.
Diagnosing brain tumors often involves imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan. Treatment options range from surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, and mainly depend on the tumor location, size, type, and the overall state of the dog.
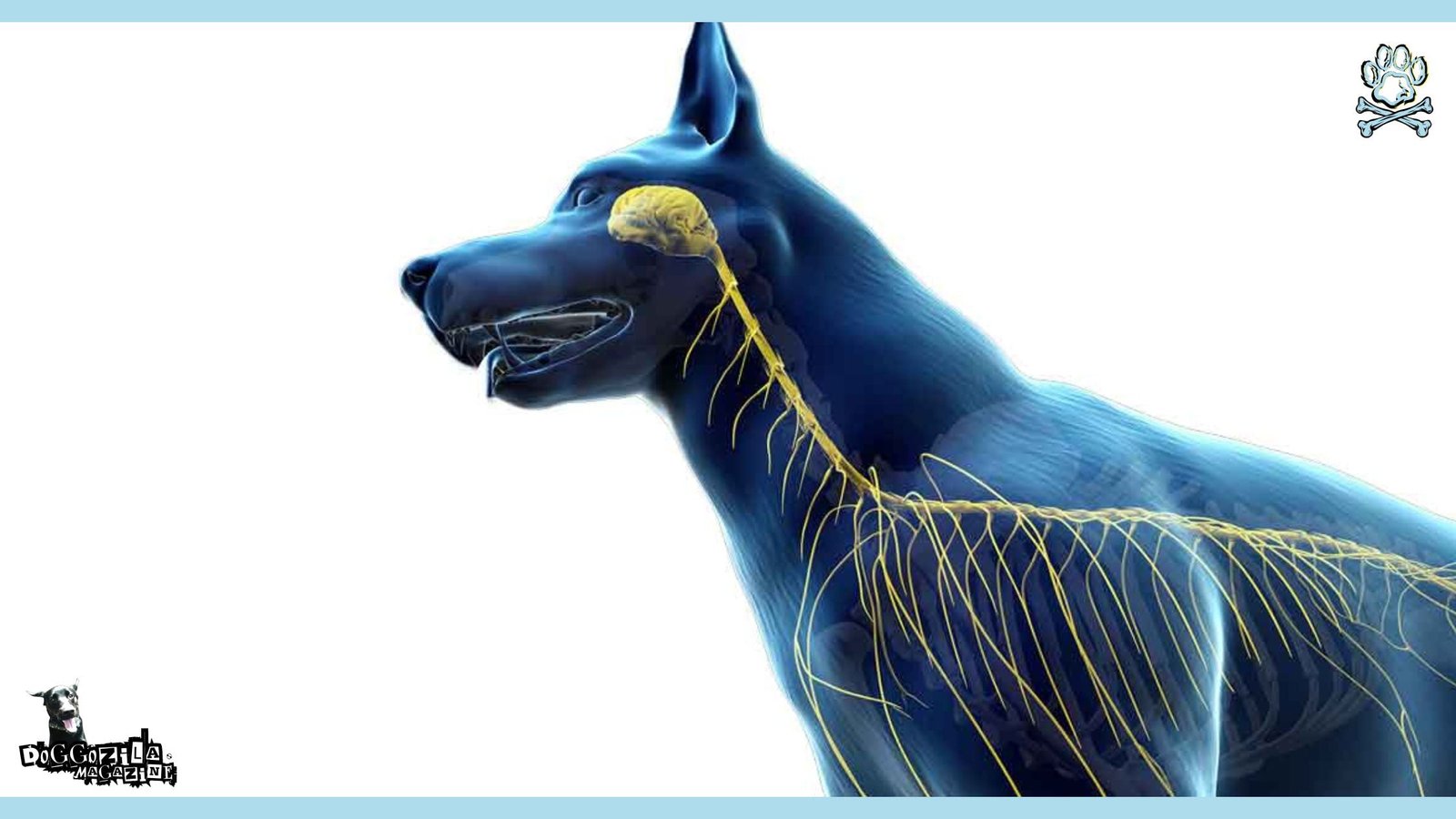
Signs and Symptoms of Neurological Disorders in Dogs
The earlier you recognize signs and symptoms of neurological diseases, the better the outcome for your pet. Address every change in behavior and pay close attention to your dog. If you’re concerned, take it to the vet for a check-up.
Recognizing Early Symptoms
When you get sick, you normally get the same symptoms every time: you feel weak, have a runny nose, cough, temperature, and body aches. As the sickness progresses, you get specific symptoms and you can determine whether it’s the flu, sore throat, bronchitis, or something completely different. The same goes for your pet. Early signs of neurological disease in dogs can vary greatly, depending on their age, type, and overall health.
Sickness in pets can manifest in a physical or a mental way, and as a pet owner, you should watch out for any changes in your four-legged friend. If your hyperactive pet suddenly starts sleeping all the time, doesn’t want to play with you, or doesn’t get the zoomies when you prepare to go for a walk, then it’s time to take it to the vet for a check-up.
A dog that suddenly seems unable to control its hind legs or bladder may be facing something as simple as a cold or an infection, or it can be something more serious such as vestibular disease, or other neurological disorders.

Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Diseases
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases can prevent further deterioration of a dog’s condition and improve its quality of life.
Diagnostic Tests for Neurological Disorders
Veterinarians employ different types of tests to detect neurological diseases in dogs. MRIs, CT scans, and spinal taps are often utilized to detect problems with the spinal cord, brain, and other parts of the nervous system. These tests help veterinarians precisely detect the disease and provide pets with specific treatment options.
Treatment Options
Once the veterinarian detects what kind of disease your pet is fighting, they’ll propose a targeted treatment option. For instance, epilepsy is typically managed with drugs to prevent seizures, while diseases like IVDD might need an operation procedure. To make the treatment option easier and less invasive, it’s important to spot signs of diseases as soon as possible.
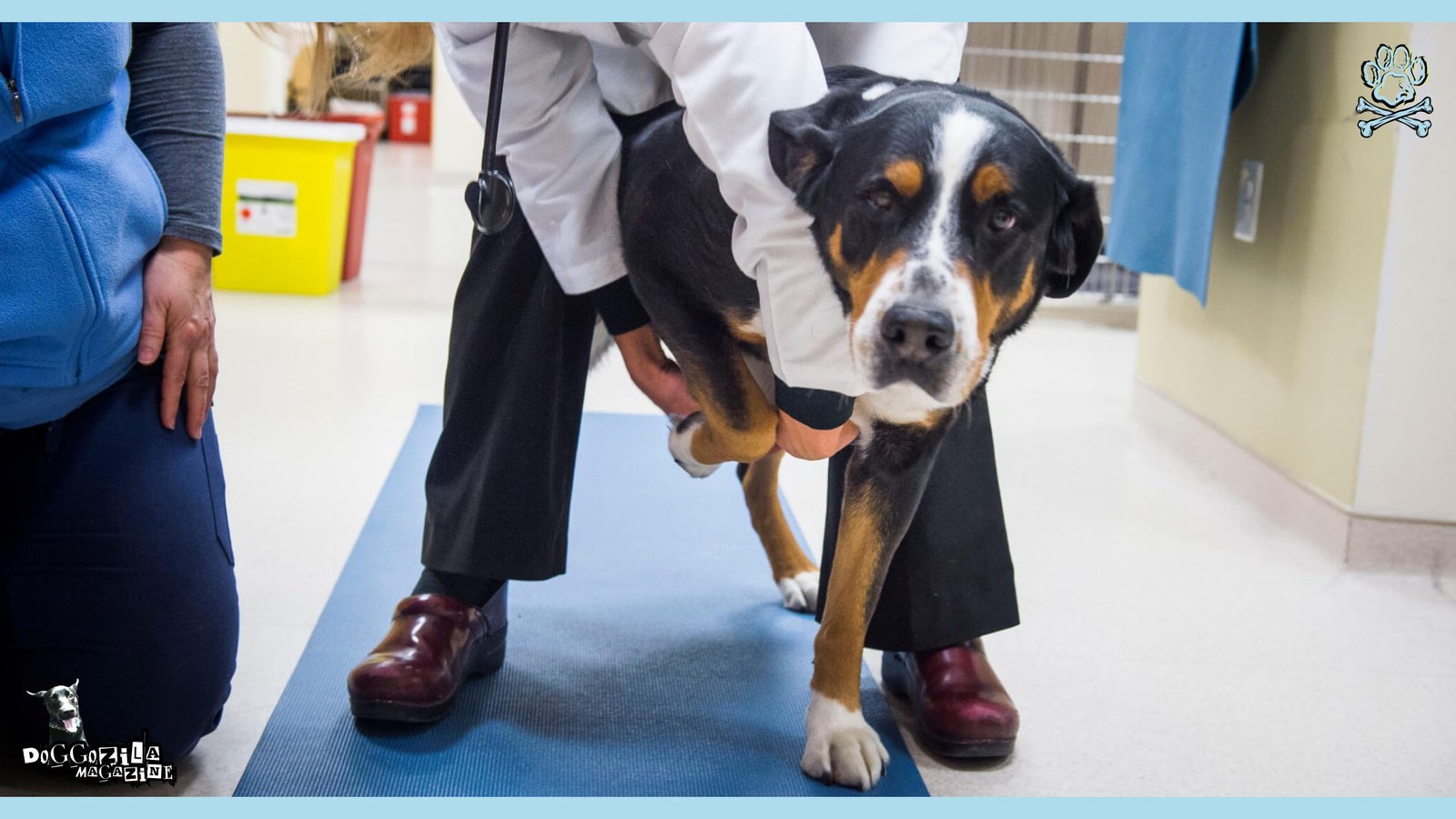
Preventing Neurological Disorders in Dogs
While some neurological diseases cannot be prevented, proactive care can reduce the likelihood of certain conditions developing.
Genetic Testing and Breed Predisposition
Certain types of breeds naturally have a higher chance of getting particular brain disorders, for instance, degenerative myelopathy and IVDD in French bulldogs. By doing gene testing and using controlled breeding methods, we can lessen these diseases in the coming generations.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular trips to the vet are very important for detecting every disease at its beginning stage. Having normal check-ups combined with a balanced diet, physical activity, and mental exercises can assist in keeping a dog’s emotional health and overall well-being.

Wrap Up
Neurological diseases in dogs, such as epilepsy, IVDD, degenerative myelopathy, dog vestibular syndrome, and brain tumors deeply affect a dog’s mental, physical, and emotional health. Regular vet check-ups, early disease detection, treatment, and prevention of diseases can improve your dog’s quality of life. By staying informed about most common diseases in dogs, and knowing your pet by heart, you’ll provide it with the best life possible, and in return, it’ll give you some of the best memories in your whole life.









